Safe zones for pin placement in the mandible
1. Safe zones for pin placement (external fixator)
Safe zones
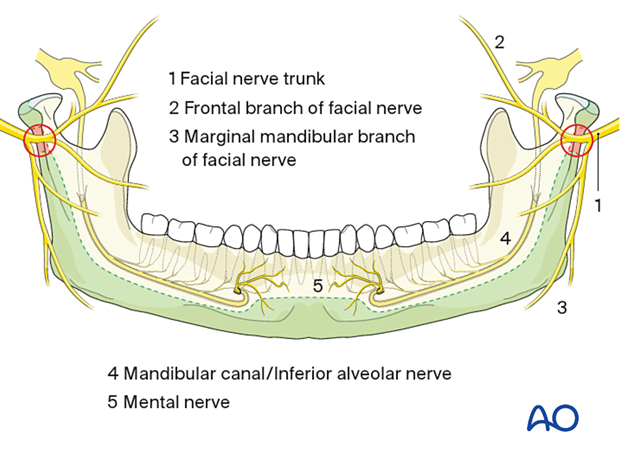
The safe zones for pin placement are located circumferentially along the lower and posterior borders of the mandible and the condylar processes. The condylar process itself can be used for K-wires outside the joint capsule.
The posterior border of the ramus and the bone in the lower border of the outer angle region have the thinnest cross-sectional dimension of the whole safe zone, but the intrabony nerve structures are running in a curvature located superiorly and medially.
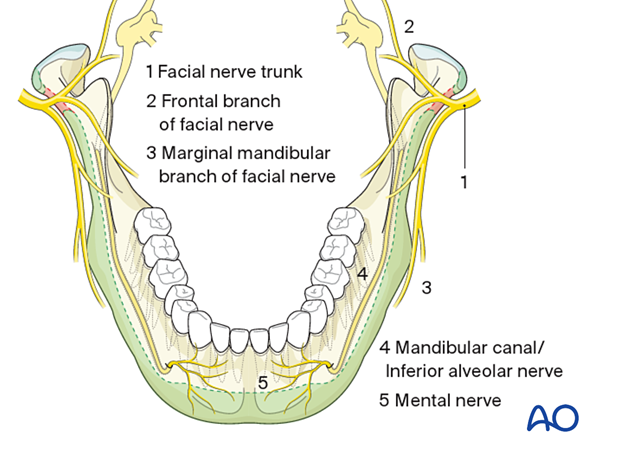
High-risk zones for nerve injury
One zone in the subcondylar neck is crossed by the facial nerve trunk in an anterior-posterior direction, representing a high-risk zone for nerve injury. Therefore, this area should be avoided.
The mandibular canal containing the inferior alveolar nerve limits the safe zone's vertical height cranially in the mandibular body and angle.
The vicinity of the mental foramen should be avoided due to individual variations in the mandibular canal course. The mental foramen generally lies between the two pre-molars.
The inferior alveolar nerve courses inferior and anterior to the foramen before exiting. The safe zone for placement of bicortical screws or pins is at least 5-6 mm caudal to the foramen.
Although there is a tiny continuation of the mandibular canal (incisal canal) in the symphyseal area, the whole bone stock beneath the tooth apices is available for pin placement.
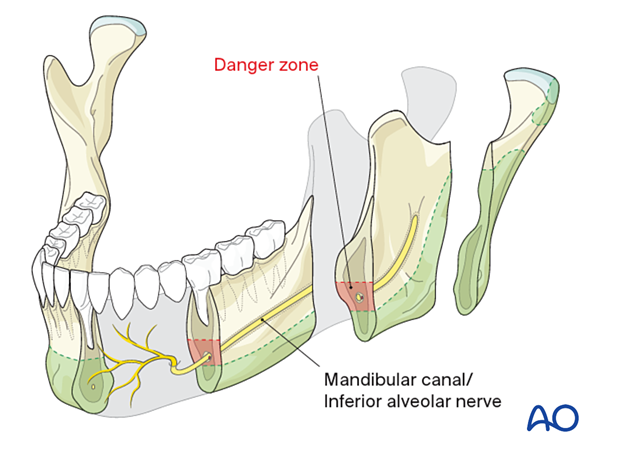
2. Bony cross-sections and intraosseous structures to avoid
The following structures should be avoided:
- Tooth roots
- Mandibular canal/inferior alveolar nerve (danger zone)
See also:
Mund Kiefer Gesichtschir; 5(3):180-5.
The following test TEST












