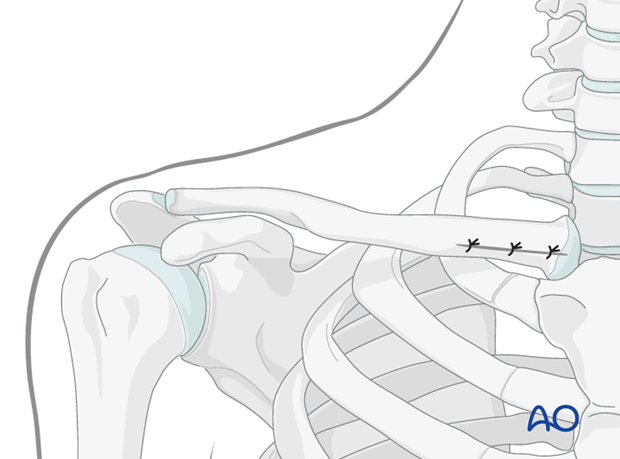
Nailing approach to the clavicle
1. Indication
This approach is used for intramedullary nailing of the clavicle.
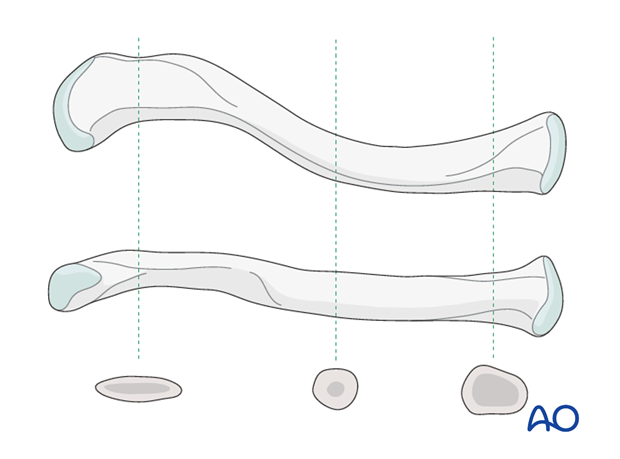
2. Anatomy
The clavicle is an S-shaped bone, anteriorly concave laterally and anteriorly convex medially. The cross sectional anatomy along its lateral to medial course changes from flat to tubular to prismatic. The junction from the flat region to the tubular region is a stress riser and this explains the higher incidence of midshaft fractures.
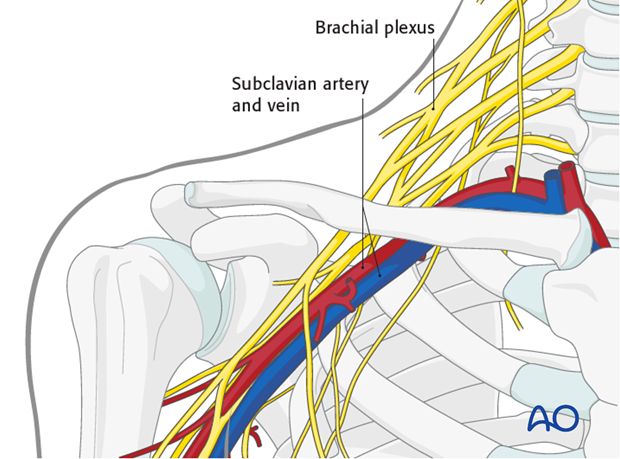
The neurovascular structures, namely, the subclavian artery and vein and the brachial plexus, pass from a posterosuperior to posteroinferior direction, between the first rib and the clavicle at the junction of its medial and middle thirds and are thus vulnerable during surgery and instrumentation in this region. In the middle third or the tubular portion, the subclavius muscle and fascia protect the neurovascular structures from the fracture. However, to avoid injury to the neurovascular structures care should be exercised when sharp instruments are used in this area.
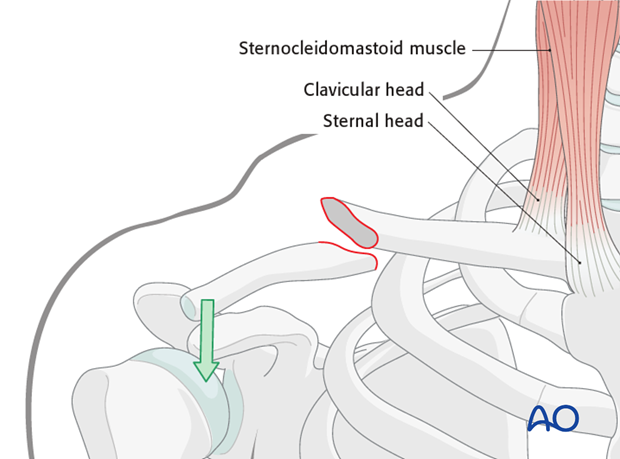
The sternocleidomastoid muscle, which inserts on the medial third of the clavicle, acts as a deforming force, pulling the medial fragment superiorly, following a fracture. The weight of the arm acts as a deforming force pulling the lateral fragment inferiorly and anteriorly. Pushing of the shoulder upward helps to reduce the lateral fragment to the medial fragment.
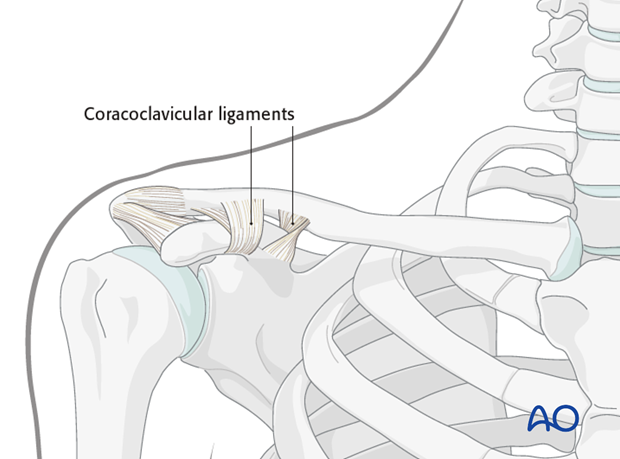
There are numerous ligamentous attachments to the clavicle in which the coracoclavicular and acromioclavicular ligaments have a dominant role in stabilizing the clavicle laterally.
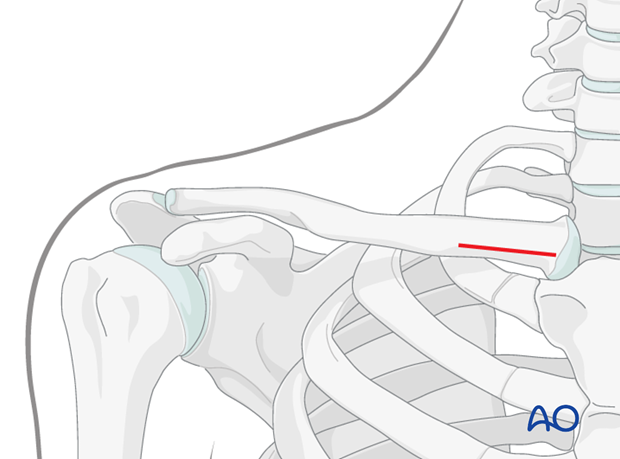
3. Skin incisions
A small skin incision, 1-2 cm in length, is made just lateral to the sternoclavicular joint anteriorly. Blunt dissection to bone is performed to expose the entry point of the nail.

4. Closure
After irrigation of the wound, it is closed in layers.