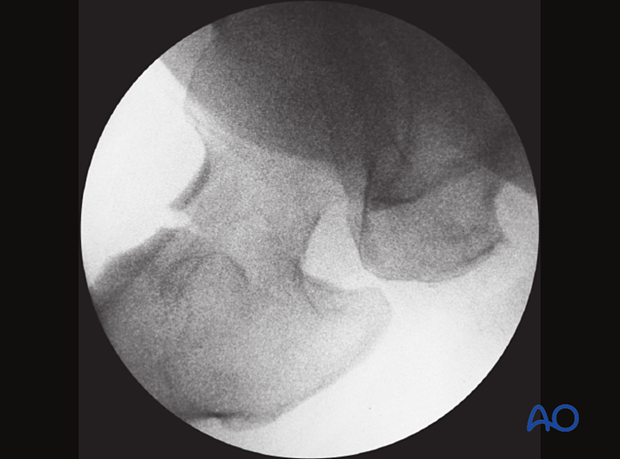
Assessment of reduction quality (femoral neck fractures)
1. General considerations
It is important to assess the reduction quality correctly and repeatedly (to recognize intraoperative redisplacement).
The following displacement patterns should be identified:
- Discontinuing cortical lines (eg, gaps and step-offs)
- Overlapping fragments
- Translation and retroversion
- Angulation (especially varus)
For C-arm positioning to acquire optimal AP, lateral, and axial views, read the additional material on:
2. Reading the fracture lines
Read the fracture line on the image intensifier views. Identify gaps or increased density due to overlapping of fragments.
Follow the medial and the lateral cortical lines on the AP view and the anterior and posterior cortical lines on the axial view. Identify any translational and angular malalignment.
The cortical lines should show intact Lowell’s S-patterns (“lazy S”) in both views.
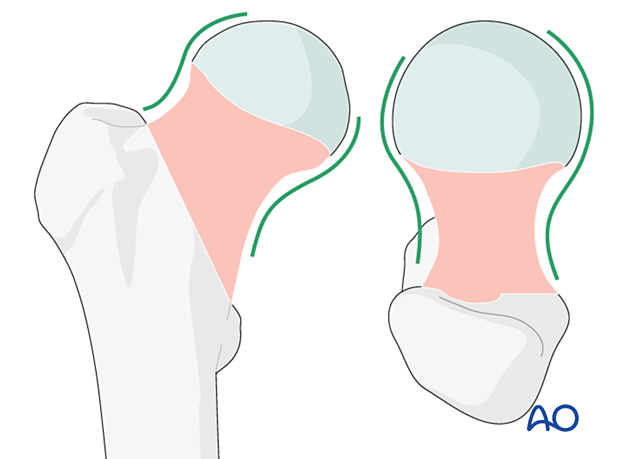
3. Acceptable reduction
Acceptable reduction quality shows the following patterns:
In the AP view:
- Continuous medial and lateral cortical lines
- No varus angulation
In the lateral view:
- Normal anteversion
- No retroversion
- Continuous anterior and posterior cortical lines
This case shows anatomical reduction in the AP and axial/lateral view with continuous cortical lines.
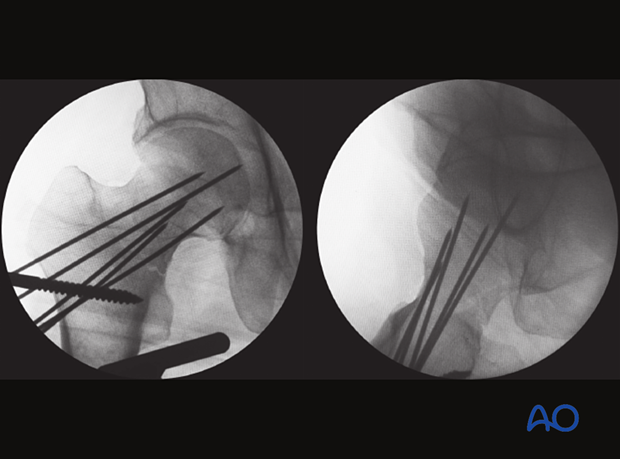
4. Displacement patterns (case example)
Discontinuous cortical lines
In the AP view, the fracture shows a shortening step in the medial cortex and a gap in the lateral cortex.
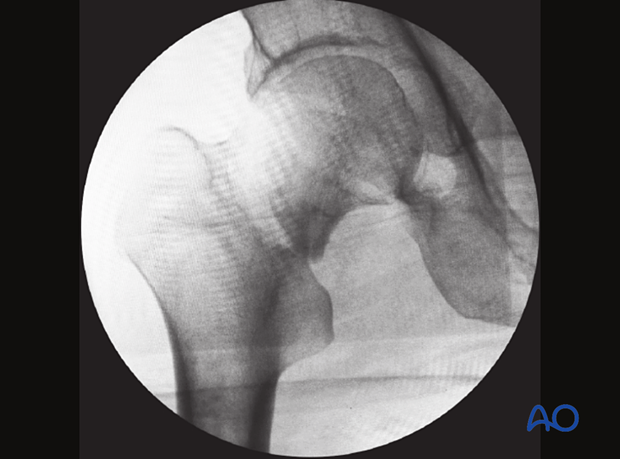
The axial view shows retroversion with a gap in the anterior cortex.