Dorsoulnar approach to the MCP joint of the thumb
1. Indications
This approach is indicated for
- intraarticular fractures in the ulnar margin of the head of the first metacarpal
- avulsion fractures of the base of the proximal phalanx
- Avulsion of the attachment of the ulnar collateral ligament to the base of the proximal phalanx of the thumb (Stener’s lesion, gamekeeper’s thumb, or skier’s thumb).
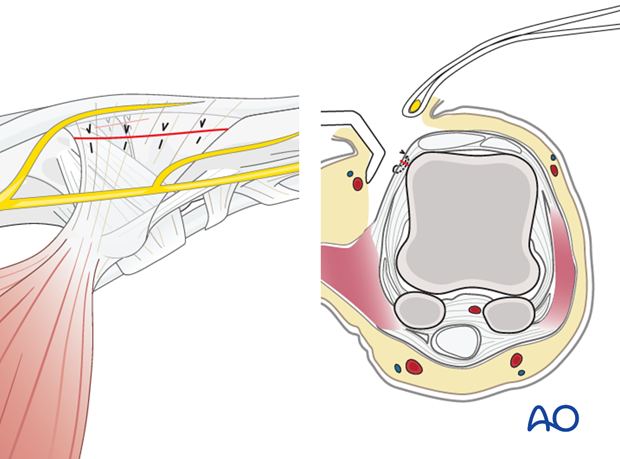
2. Surgical anatomy
On the ulnar aspect of the metacarpophalangeal (MCP) joint of the thumb are seen the transverse and oblique fibers of the adductor pollicis aponeurosis (and some muscle fibers), inserting into the extensor pollicis longus (EPL) tendon, and all overlying the ulnar collateral ligament.
Divisions of the dorsal sensory branch of the radial nerve lie superficially in the subcutaneous tissue of this region.
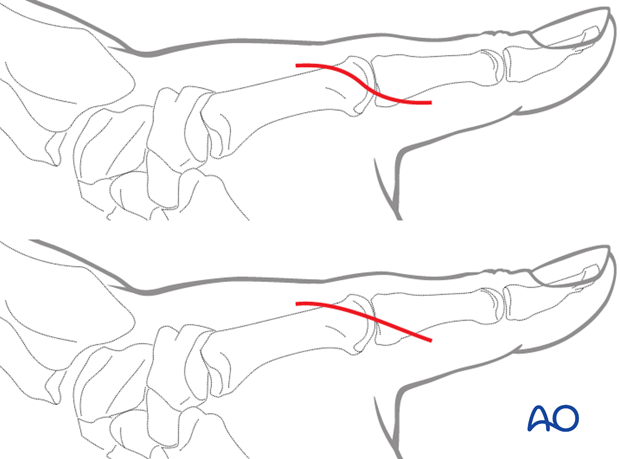
3. Skin incision
An incision starting dorsally, about 1 cm proximal to the MCP joint is extended in a palmar direction around the ulnar aspect of the join, to about 1 cm distal to the joint.
The incision can be oblique or of a lazy S-shape.
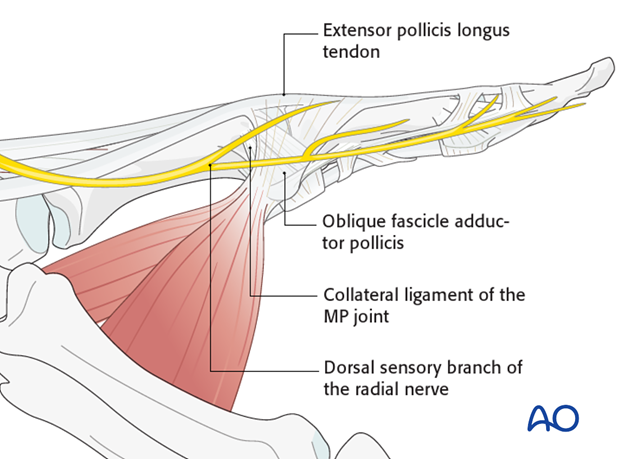
4. Identifying the structures
Identify and protect divisions of the dorsal sensory branch of the radial nerve, using a vessel loop.
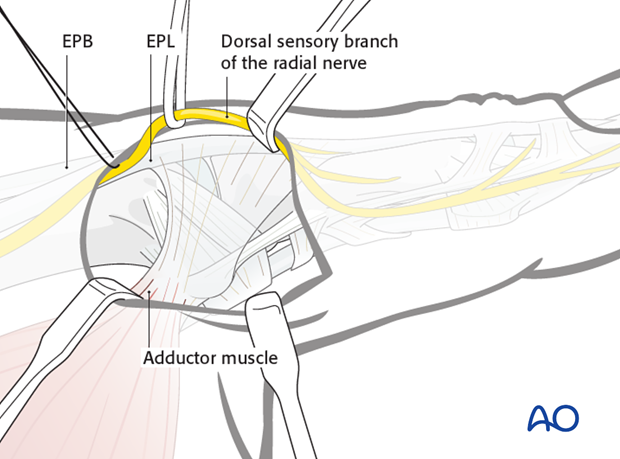
Identify the adductor pollicis muscle with its aponeurosis, as well as the tendons of EPL and EPB.
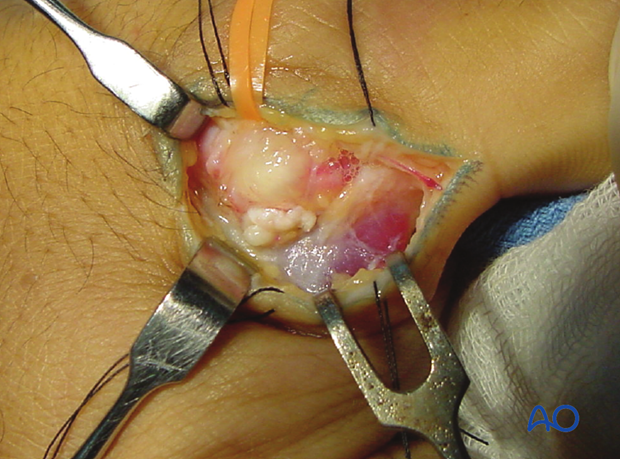
5. Elevation of the aponeurosis
A dental pick is inserted deep to the aponeurosis of the adductor pollicis longus (APL) and between it and the ulnar collateral ligament and dorsal capsule.
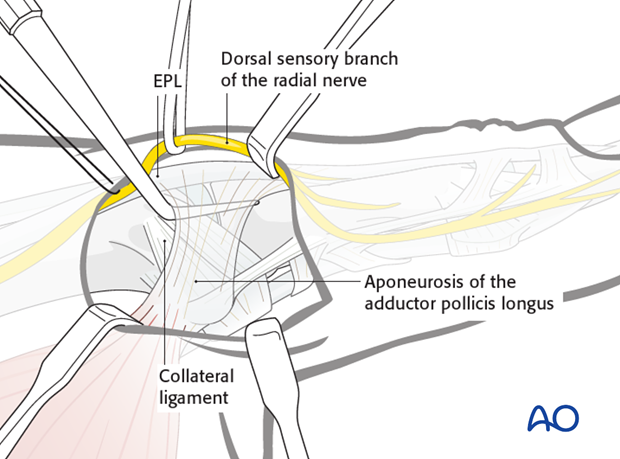
This protects the underlying structures when the adductor aponeurosis is divided.
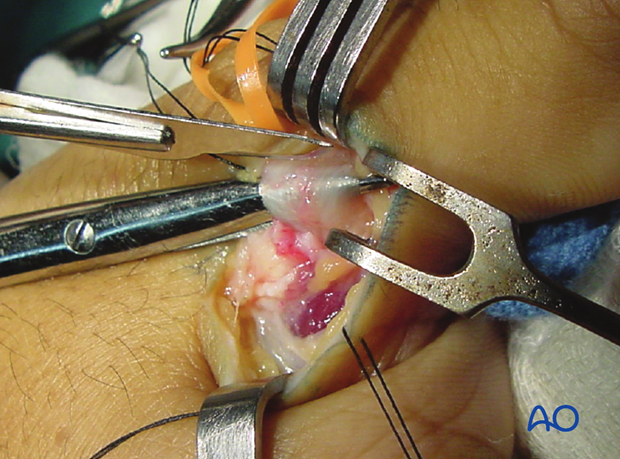
6. Division of the adductor aponeurosis
Make a longitudinal incision to divide the adductor aponeurosis close to its insertion into the EPL tendon.
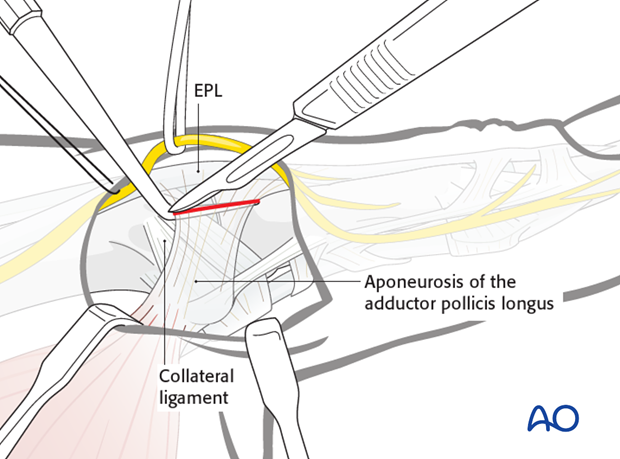
Leave a 3-5 mm fringe for later reattachment.

7. Exposure of the ulnar collateral ligament
Retract the aponeurosis in a palmar direction using fine sutures, ...
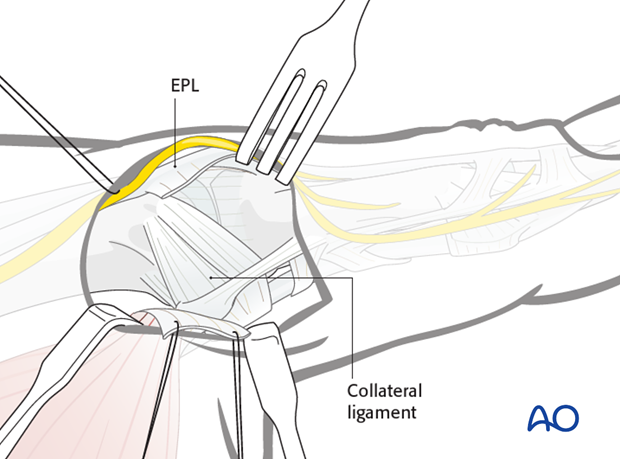
... and pull EPL dorsally with a small retractor, exposing the ulnar collateral ligament and dorsal capsule.
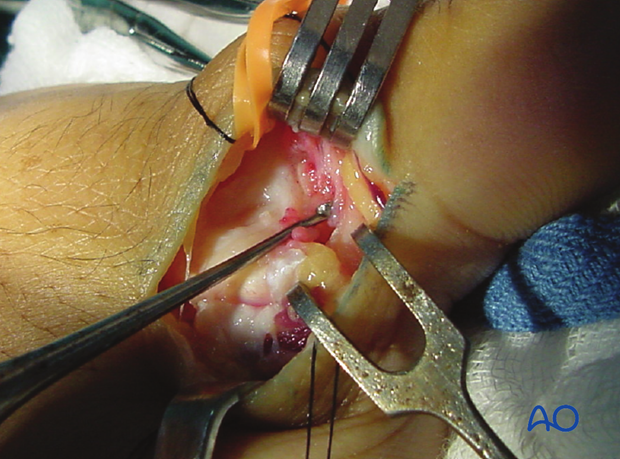
8. Capsulotomy
Make a longitudinal dorsal capsulotomy, avoiding disinsertion of the proximal attachment of the collateral ligament into the metacarpal tubercle.
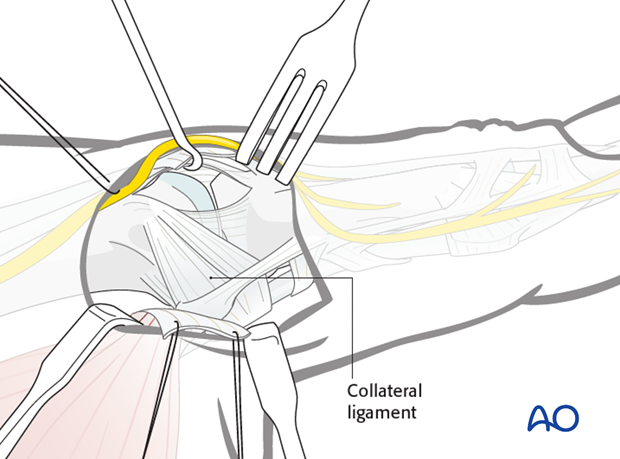
9. Wound closure
Close the capsule and then reattach the adductor aponeurosis using fine interrupted mattress sutures.