Anteromedial approach to the pediatric distal tibia
1. General considerations
Introduction
The anteromedial approach is useful for the treatment of most distal tibial fractures that extend medially.
Surgical approach
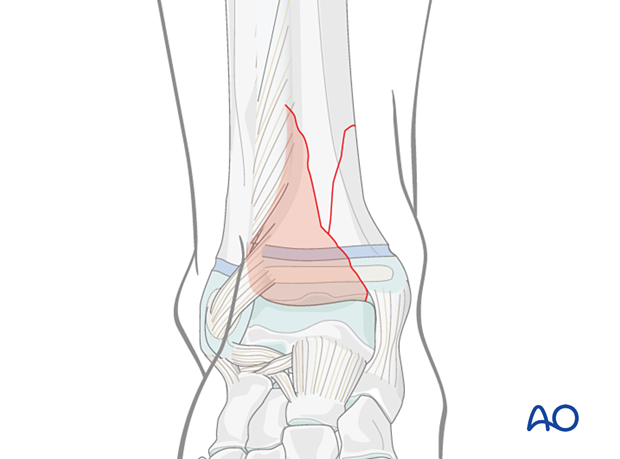
Most distal tibial fractures are approached either anteromedially or anterolaterally. The size of the anterolateral fragment helps to determine the optimal approach.
When the fragment is large and the medial fracture plane is at or near the medial malleolus, an anteromedial approach is recommended.
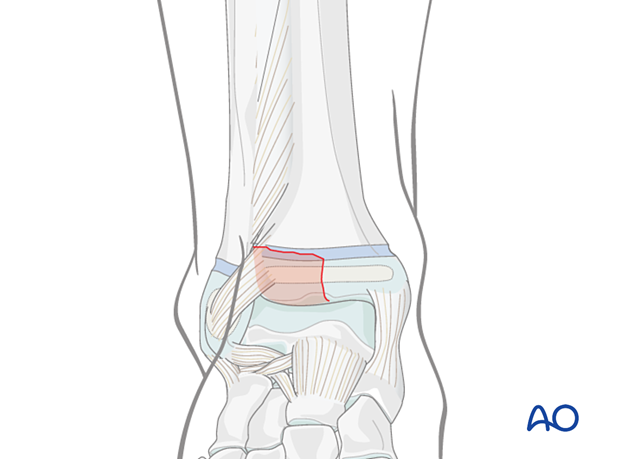
When the anterolateral fragment is smaller and the fracture reaches the articular surface more laterally, reduction can be achieved with an anterolateral approach.
Precautions
The lower tibia does not have muscle cover and preservation of the blood supply is crucial. Minimal exposure and careful handling of the periosteum are essential to prevent further soft-tissue damage.
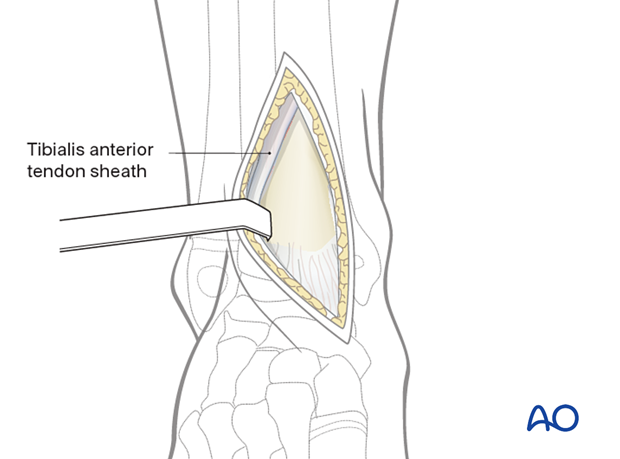
Preserve the tibialis anterior tendon sheath to avoid postoperative adhesions and tendon attrition.
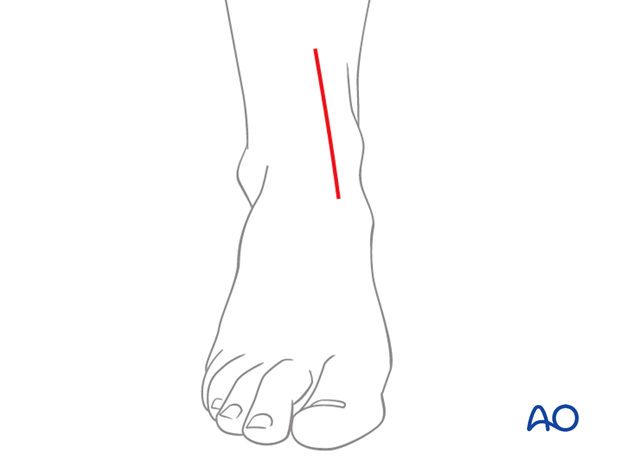
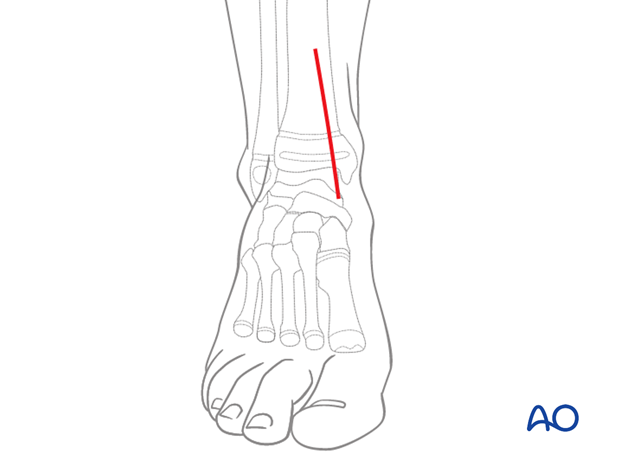
2. Skin incision
Incise the skin, centered over the fracture in a straight line following the medial border of the tibialis anterior tendon.
The length of the incision depends on the position of the fracture, implant and leg size.
3. Surgical dissection
Dissection through the skin and subcutaneous tissues should preserve full-thickness skin flaps.
Deepen the dissection through the extensor retinaculum to the periosteum, just medial to the tibialis anterior tendon.
It is critical to leave the tendon sheath intact and immediately repair any traumatic or inadvertent disruption that directly exposes the tendon.
Lateral dissection between the posterior border of the tendon sheath and the periosteum may be required to reduce a large anterolateral fragment. A separate, small anterolateral incision may be necessary for fixation.

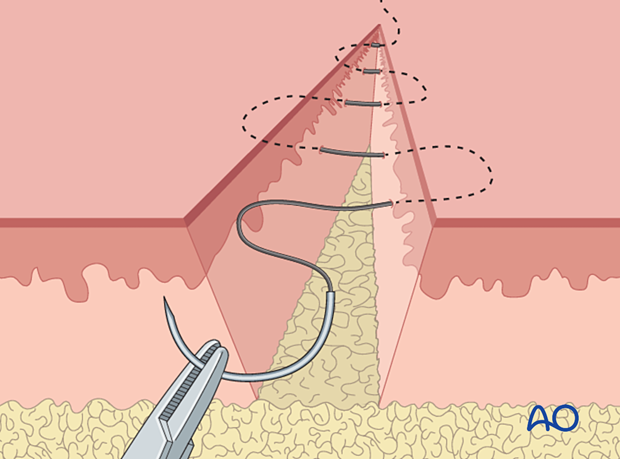
4. Wound closure
After careful hemostasis, close the subcutaneous tissue and skin separately. Subcuticular, absorbable skin sutures may be used if the condition of the soft tissues permit it.