Entry points for antegrade elastic nailing of the pediatric tibia
1. General considerations
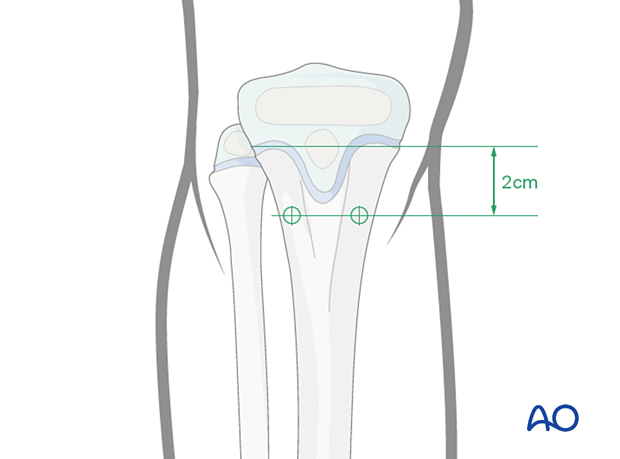
For fractures stabilized with two antegrade elastic nails, the entry points are in the proximal metaphysis of the tibia.
The medial and lateral entry points are 2 cm distal to the proximal tibial physis, avoiding the cartilage of the apophysis. The lateral entry point may be more anterior due to muscle coverage.
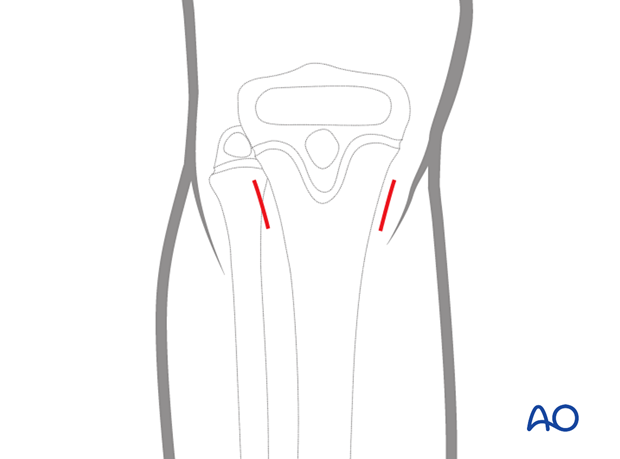
2. Skin incision
Make a skin incision on the medial and lateral side of the proximal tibia, starting at the entry points and extending 2 cm proximally. This allows sufficient space to advance the nails at an angle to the cortex.
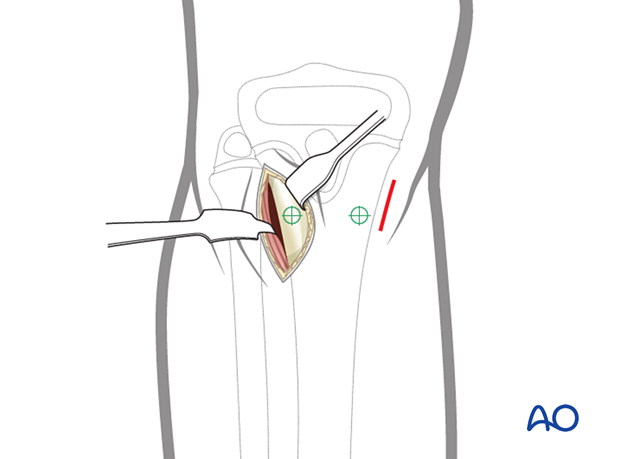
3. Subcutaneous dissection
Dissect the subcutaneous tissue until the cortex of the tibia is reached.
On the medial side, this is a direct dissection down to the bone. On the lateral side, retract the muscle laterally away from the cortex.
On the lateral side, the entry point is slightly anterior due to the extensor muscles, which are retracted laterally.
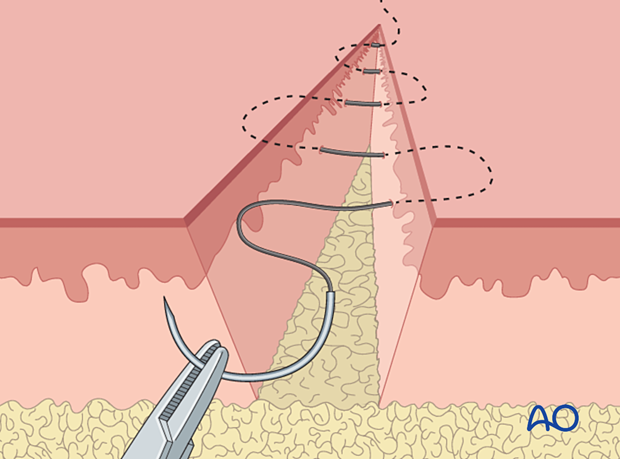
4. Wound closure
After careful hemostasis, close the subcutaneous tissue and skin separately. Subcuticular, absorbable skin sutures may be used if the condition of the soft tissues permit it.