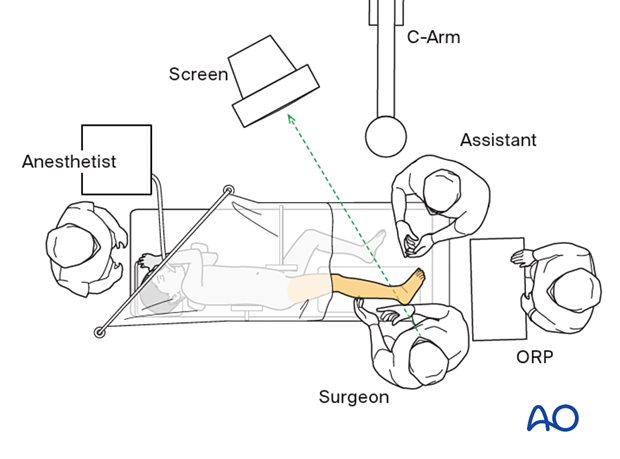
Patient preparation in lateral decubitus position
1. Introduction
The lateral position provides good access to the fibula and posterior part of the tibia and is used for the lateral and posterolateral approaches.
2. Preoperative preparation
Read the additional material on preoperative preparation.
3. Anesthesia
The addition of regional and local anesthesia may reduce postoperative pain.
4. Prophylactic antibiotics
Antibiotics are administered according to local policy and specific patient requirements.
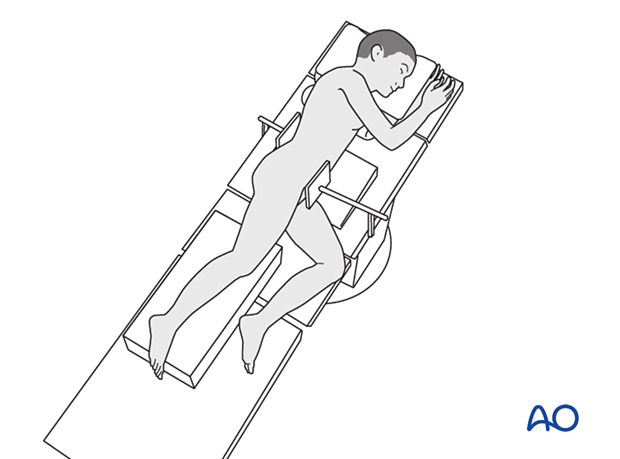
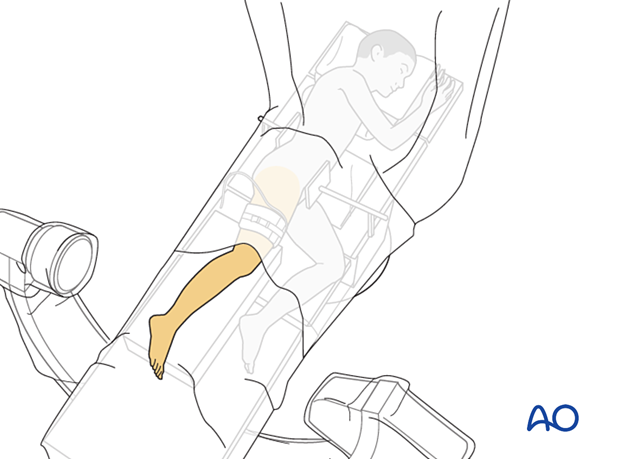
5. Patient position
Place the patient in a lateral position on a radiolucent table with supports on the lumbar spine and the anterior superior iliac spine (ASIS).
The contralateral shoulder must be carefully positioned to prevent brachial plexus injury. Add a bolster or roll under the thorax to minimize the pressure on this shoulder.
Bolsters, pads, or a bean bag can be used to position and protect the pelvis.

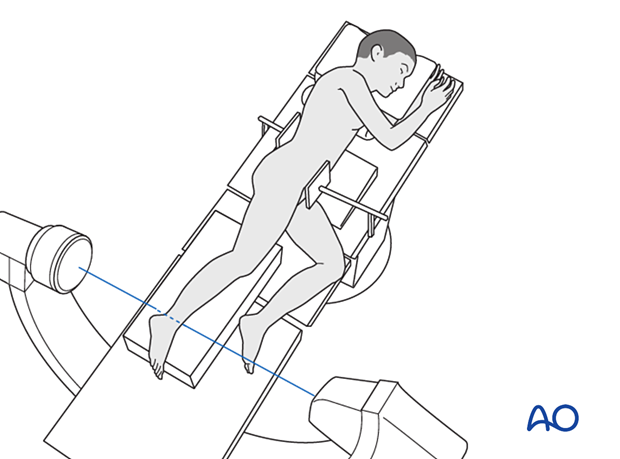
6. C-arm positioning
Position the C-arm so that AP and lateral views can be obtained without moving the leg.
7. Tourniquet
Tourniquet use depends on the morphology of the fracture and soft-tissue injury. This can reduce blood loss and improve visualization of the articular surface.
The effect of ischemia/reperfusion in the presence of a compromised soft-tissue envelope must also be considered.
Tourniquet width should be more than half the limb diameter and applied over a thin layer of padding.
The ischemic time should be less than 120 minutes.
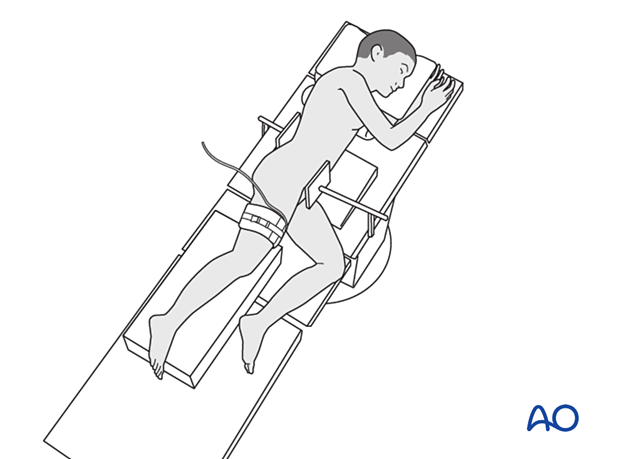
8. Skin preparation and draping
Prepare the entire leg, including the foot.
Drape the leg to the mid-thigh or the level of the tourniquet.
Drape the C-arm in a conventional manner.
9. OR set-up
The optimal position of the surgeon is behind the patient, with the injured leg slightly flexed and adducted.
The position of the image intensifier screen should allow a direct view for the surgeon.