Clinical evaluation
1. Overview
Femoral fractures, especially in the nonwalking child, require a careful history and detailed physical examination.
The examination must be of the whole child to exclude additional injuries that may not be accidental.
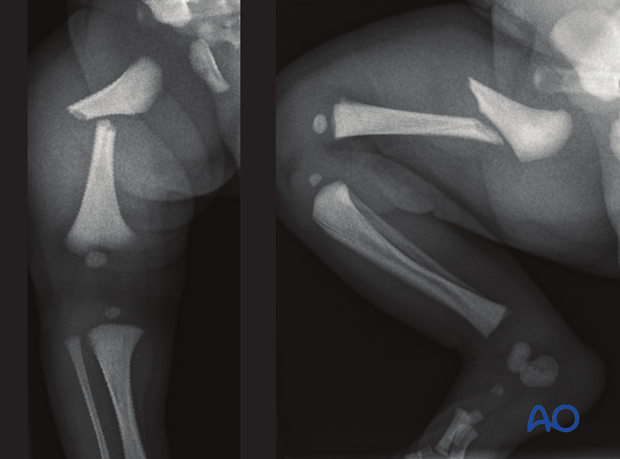
2. Associated conditions
Comorbidities should be considered in children with femoral shaft fractures (eg, osteogenesis imperfecta).
3. Symptoms
- Thigh pain
- Knee pain
- Limb Deformity
- Inability to walk
4. Physical exam
Check for soft-tissue injuries and neurovascular compromise.
Check for additional injuries especially in high-energy accidents (ATLS).
Check for signs of deliberate injury including finger marks, fractures of differing ages, cigarette burns and perineal injury.
5. Vascular examination
Vascular injuries are uncommon with femoral shaft fractures.
Vascular consultation and arteriography may be needed in cases of vascular impairment.
If delayed reperfusion has occurred the patient is also at risk of developing a compartment syndrome of the lower leg.
See also the additional material on neurovascular anatomy.












