Combined posterior and left side
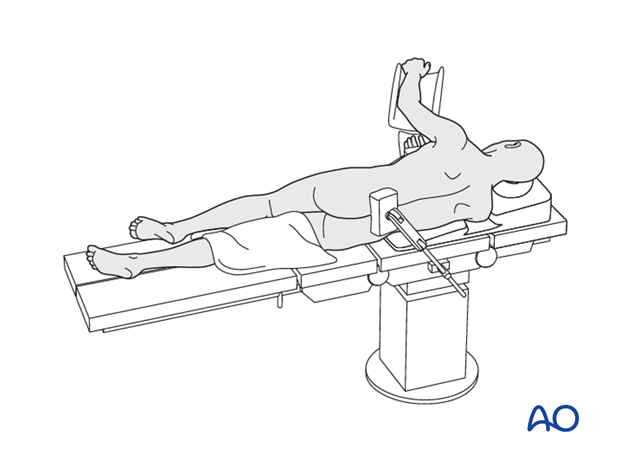
1. Patient positioning for left sided thoracotomy
The patient is placed onto a radiolucent table and turned into the lateral decubitus position, left side up.
The left arm is elevated and placed in a well-padded support and a cushion pad should be placed underneath the right axilla.
Depending on surgeon preference, the table could have a tilting option. If selected, the tilting option should be located underneath the patient's thoracolumbar junction, which gives the possibility to open the intercostal space.
The operating room should be set in a way to accommodate fluoroscopy and the thoracoscopic instruments and screen should be placed in front of the patient as surgeons usually positions themselves in the back of the patient.
Upon completion of the anterior release, the patient is positioned prone.
2. Patient positioning for posterior instrumentation
There are two options of patient position for kyphosis corrections.
The following points are common for both options:
- The abdomen should hang free to avoid high intraabdominal pressure and subsequent venus pressure causing excessive bleeding of the spine.
- The arms/shoulders should be resting comfortably in a 90-90° position of the shoulder and elbow.
- Adequate padding needs to be provided to elbows and knees to avoid pressure sores
- The toes should hang free
- The head is best placed in a face mask to avoid pressure on the eyes and have the endotracheal tube free with the neck in neutral position.
- Avoid having the head lower than the rest of the body to reduce the risk of postoperative blindness (due to high hydrostatic pressure in the eyes leading to reduced blood perfusion).
- Positioning should attempt to reduce thoracic kyphosis and optimize lumbar lordosis.
- It must be possible to obtain radiographic images in both AP
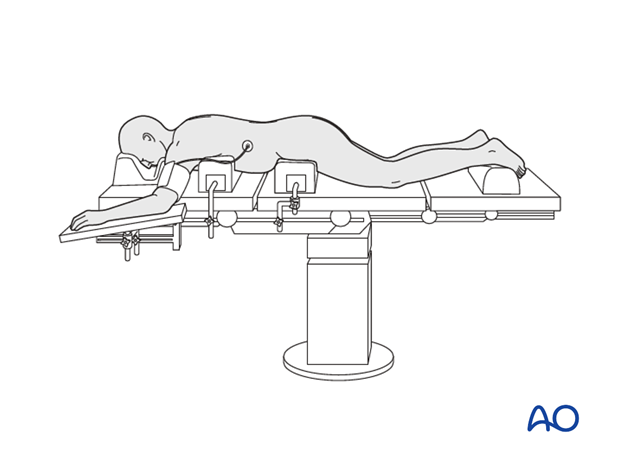
Variation 1: Bolster
The patient is placed prone on a radiolucent table with bolster support under the sternum, iliac crest, and the lower legs.
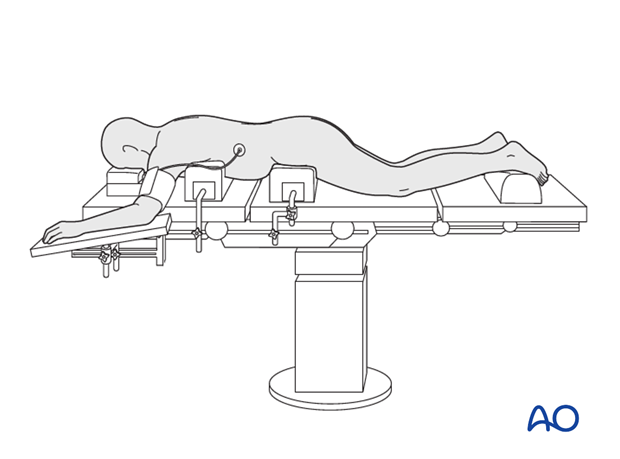
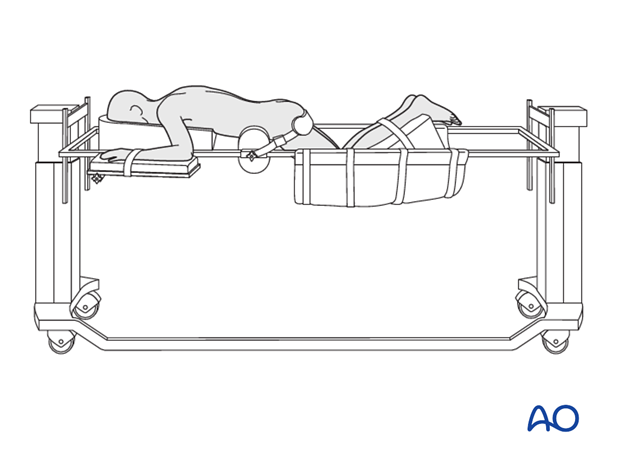
Variation 2: Jackson frame
The Jackson frame is a specialized operating table for spine surgery.
3. Anaesthesia
General anaesthesia with endotracheal intubation is required.
Anaesthesia maintenance should interfere minimally with spinal cord monitoring.
High concentrations of nitrous oxide and inhalational agents interfere with spinal cord evoked potential monitoring.
When using motor-evoked potentials, muscle relaxants should be avoided.
Techniques to minimize blood transfusion during scoliosis surgery include avoiding hypothermia, controlled hypotension, intraoperative cell salvage and pharmacological agents such as tranexamic acid.
4. Blood management
Hypotensive anaesthesia (Mean arterial pressure (MAP) of 60 – 70 mmHg should be used during the exposure. Normotensive anaesthesia is recommended during the correction procedure to optimize blood flow to the spinal cord.
The use of a blood salvage techniques (eg. cell saver) is recommended.
Anti fibrinolytics (eg. tranexaminic acid or aminocaproic acid) can significantly reduce blood loss.
5. Preoperative antibiotics
Antibiotics should be administered well prior to the incision and also at 6h intervals or when the blood loss exceeds 2L.
A cephalosporin antibiotic with good gram positive coverage is generally recommended. Local bacterial spectrum will need to be taken into account, this should be discussed with the hospital microbiologist.
6. Spinal cord monitoring
Spinal cord monitoring is implemented. The risk of spinal cord injury during kyphosis correction is significantly higher than scoliosis surgery. To monitor the integrity of the spinal cord and cauda equina intraoperative neuro monitoring should be performed.
Motor Evoked Potentials (MEP) and Somatosensory Evoked Potentials (SSEP) are optimal methods of intra-operative spinal cord monitoring.
In case of critical changes in the evoked potentials, the possibility of a wake up test needs to be available during the procedure.
In the event of signal changes, the following steps should be considered:
- Rule out equipment malfunction
- Surgical pause to reassess operative environment
- Alert anesthesiologist and surgeon
- Optimize anaesthetic agents, and patients temperature, and hemodynamic status
- Elevate blood pressure
- Reversal of any recently performed corrective maneuvers
- Rule out implant malposition
- Consider wake up test
- Consider steroid administration
- Consider radiographic evaluation
- Consider aborting procedure while providing spinal stability












