Prone
1. Prone for posterior midline approach
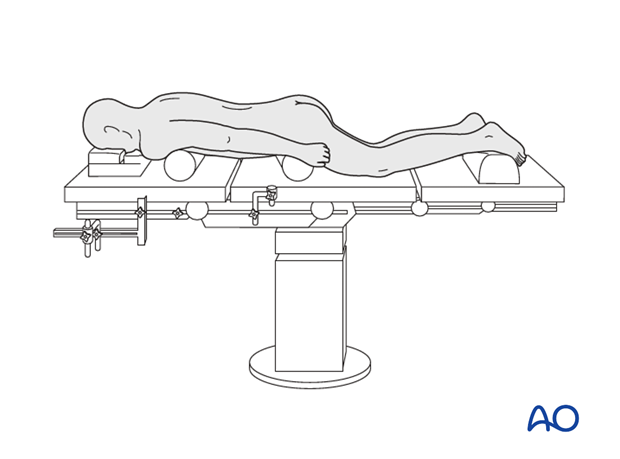
The patient is positioned onto a radiolucent table prone on two horizontally placed padded bolsters (one at the level of sternum and another one at the level of anterior iliac spine) or a frame.
- The abdomen should hang free to avoid increased intraabdominal pressure to prevent excessive bleeding
- Adequate padding needs to be provided to elbows and knees to avoid pressure sores
- The head is rested either in a horse shoe ring or a Mayfield rest to avoid pressure on the eyes.
Make sure that there are adequate personnel to receive and turn the patient from supine to prone position on the operating table. Rotational or flexion movements at the level of injury can result in worsening of neurological status.
The arms should be abducted and should be resting comfortably at 90° position of the shoulder and elbow.
The hips can be extended to partially reduce the lumbosacral kyphosis. Care must be taken as this may result in foraminal stenosis resulting in nerve injury.
2. Anaesthesia
General anesthesia with endotracheal intubation is required.
3. Preoperative antibiotics
Antibiotics should be administered well prior to the incision and also at intervals during the procedure or when the blood loss exceeds 2 liters.
A cephalosporin antibiotic with good gram positive coverage is generally recommended. Local bacterial spectrum will need to be taken into account; this should be discussed with the hospital microbiologist.
4. Spinal cord monitoring
Spinal cord monitoring is mandatory to monitor the L5 nerve root when spinal reduction is performed.
Spinal cord monitoring is also mandatory in dysplastic spondylolisthesis.
5. Fluoroscopy/x-ray control
Preoperative fluoroscopy is mandatory. Before draping, one should ensure that both AP and lateral fluoroscopy views are possible with the C-arm for all levels that are to be instrumented. Once the patient is positioned, the fractured vertebra is checked with the image intensifier to ensure it is seen clearly in both AP and lateral planes.












