Retroperitoneal approach (L4–S1)
1. General considerations
The exposure for resection of primary tumors may be wider than in a trauma approach.
An access surgeon may be helpful for this type of exposure.
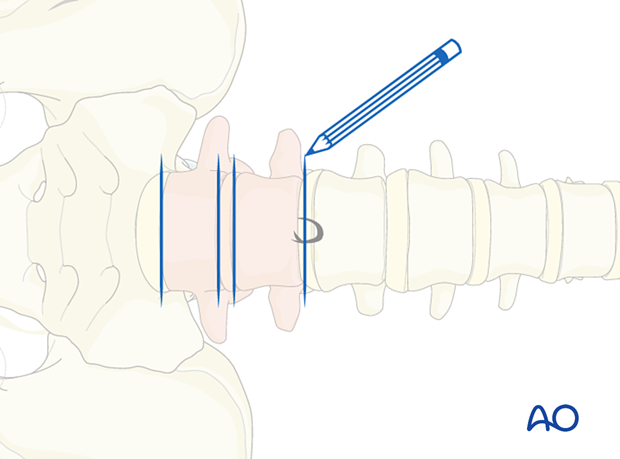
The exact incision site will depend on the area of interest. The disc space L1/2 and above cannot be reached with this approach.
The straight anterior approach (retroperitoneal approach) is excellent for corpectomy, spinal canal decompression, and vertebral body replacement. The lumbotomy is ideal for plating.
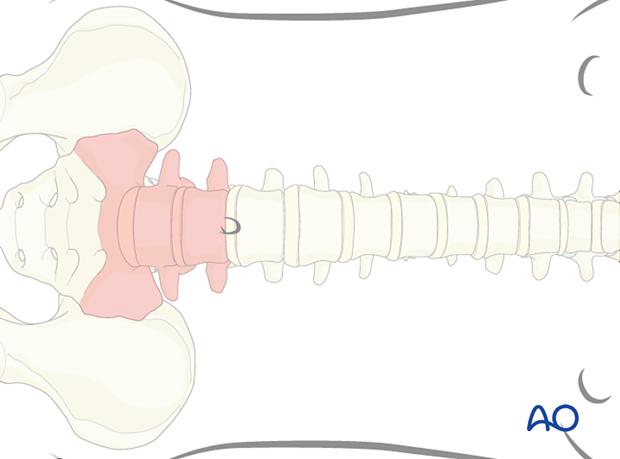
2. Skin incision
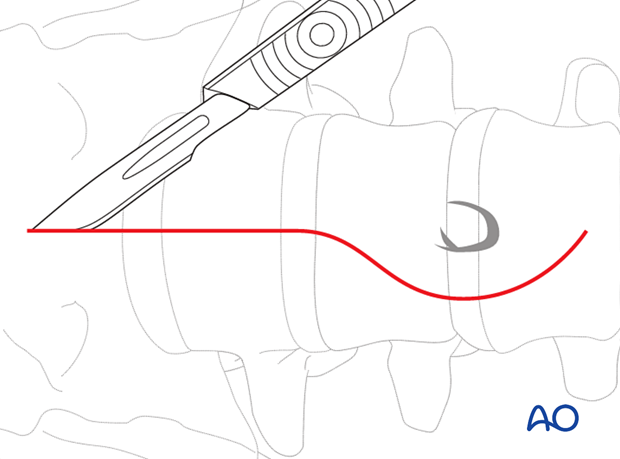
Under fluoroscopic control, the vertebra and disc of interest are marked on the skin.
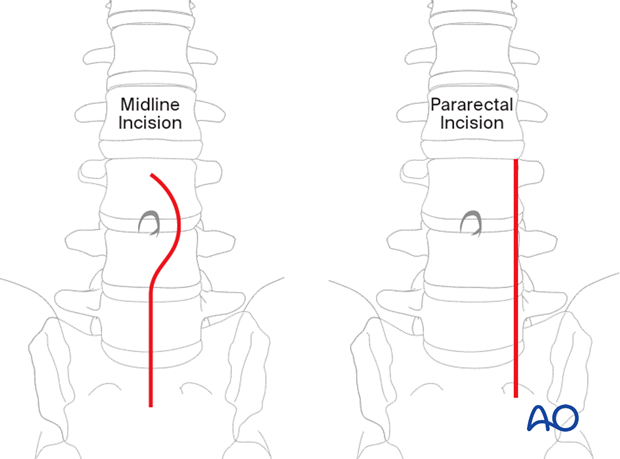
There are different options for skin incisions, depending on the preference of the surgeon and patient.
The midline skin incision and the pararectal skin incision are shown.
The skin is incised on the mark.
3. Exposure
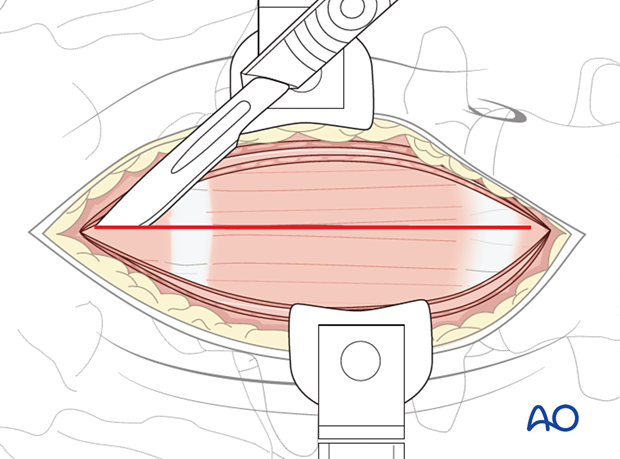
After dissection of the subcutaneous tissue, the anterior rectus sheet is incised, and the rectus muscle is mobilized to the medial or lateral side, depending on the incision and the surgeon's preference.
The posterior rectus sheet is opened, and the peritoneum is exposed.
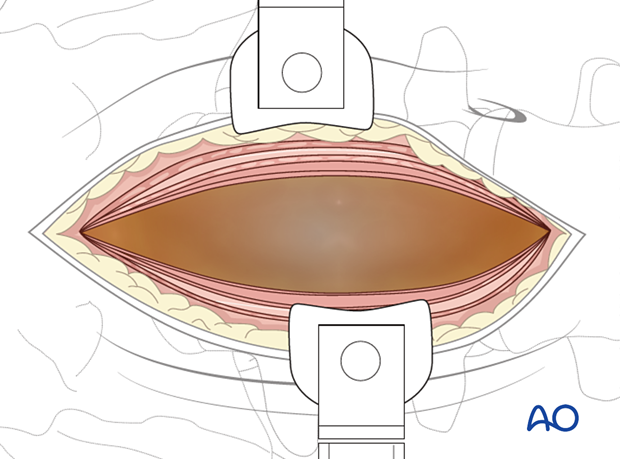
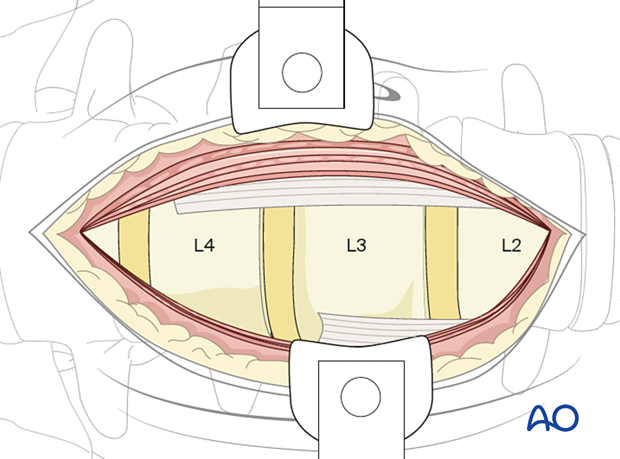
Next, the peritoneum is carefully retracted using a hand.
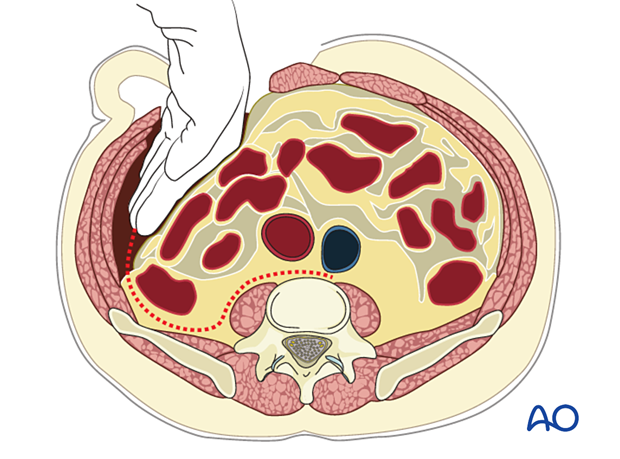
For the L4/5 level and above, vessels must be retracted to the opposite side.
For L5/S1, the vertebrae are accessed between the vessels' bifurcation.
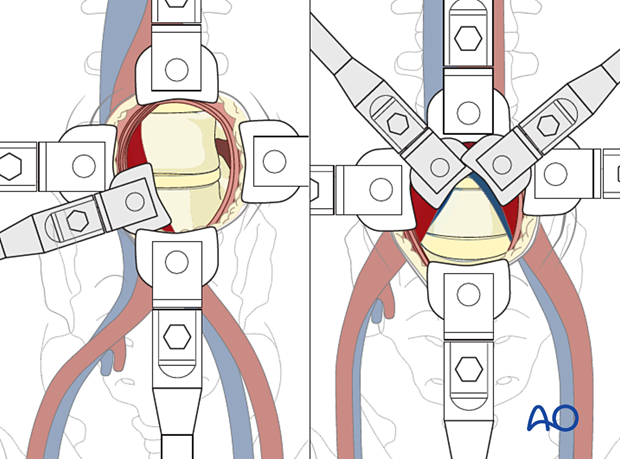
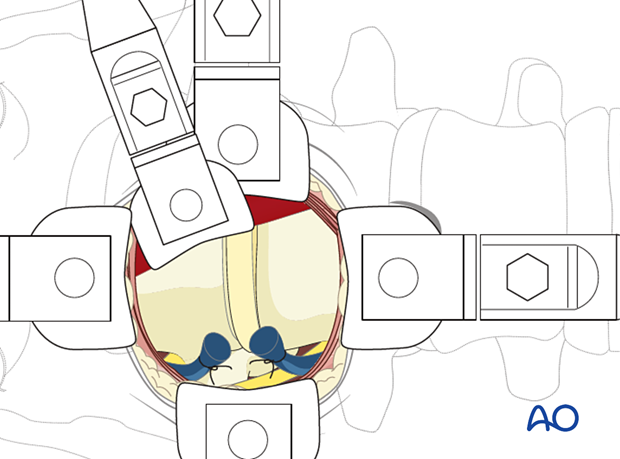
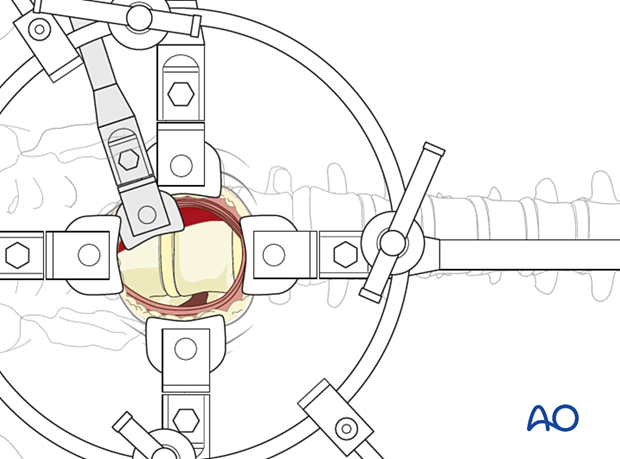
4. Retraction system
A retraction system is mandatory at this point.
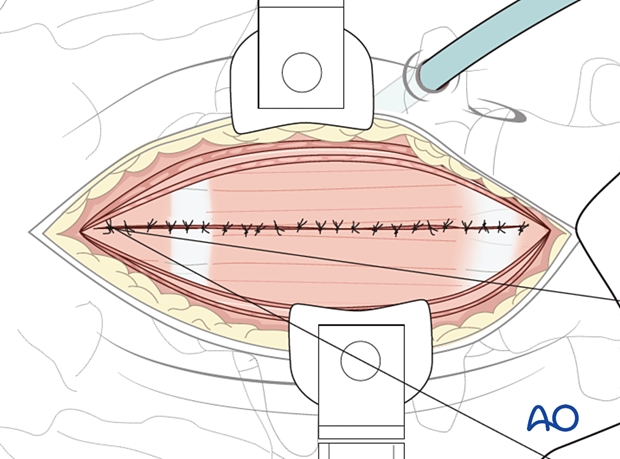
5. Closure
A retroperitoneal drain may be inserted.
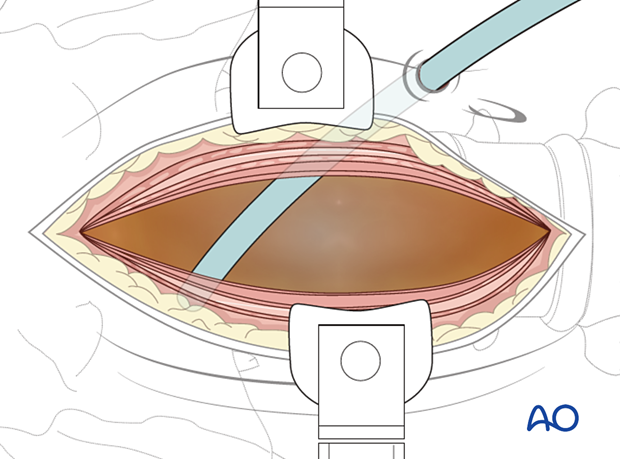
The wound is then closed in layers.